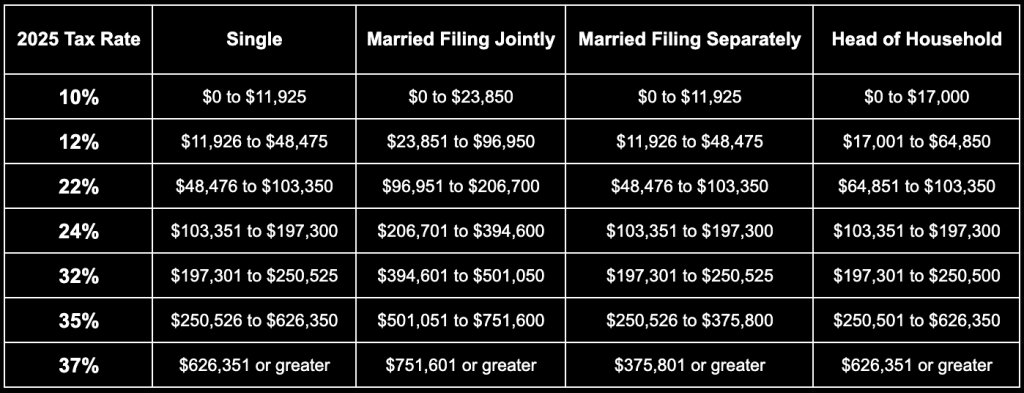
Understanding the 2025 tax brackets, seven federal income tax rates is essential in anticipation of tax season. Ranging from 10% to 37%, these rates are fixed until 2025 due to the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017. Knowing which tax bracket you fall into, how these rates function, and strategies to minimize your tax liability are important.
In the realm of taxation, individuals are subject to a spectrum of seven different income tax rates, spanning from 10% to 37%. As one delves into the complexities of tax preparation, it becomes imperative to discern the federal income tax bracket(s) in which one falls, comprehend the nuances of tax rates, and explore strategies to minimize the tax burden.
In contrast, various portions of your income may be grouped into separate categories, leading to the possibility of being taxed at different rates on different segments of your overall earnings. The amount you owe in taxes is influenced by your income level and filing status. Explore the IRS tax tables and brackets for the year 2025 provided further on, and also track the evolution of tax brackets over previous years to gain insights into how they have evolved over time.
2025 Tax Bracket Breakdown
In the upcoming year of 2025, the tax brackets for that specific period will be applicable to the income acquired during said year. Taxpayers filing their tax returns in 2026 will report the income earned in 2025.
First, What Is the Income Tax Bracket
In the United States, the tax system is designed to be progressive, where individuals with higher earnings face higher federal tax rates. At the same time, those with lower incomes encounter lower tax rates. Tax liabilities are determined by dividing taxable income into sections, referred to as tax brackets, with each section being taxed at a specific rate set by the government.
Tax rates encompass a spectrum, spanning from 10% to 37%. One significant aspect of tax brackets is that irrespective of the bracket(s) you fall into, you typically do not pay that particular tax rate on your entire earnings. Instead, the highest tax rate is typically applied to only a fraction of your income.
How do the 2025 Tax Bracket and Rates work On The State Level?
Similar to the federal system, many states in the U.S. implement a progressive income tax structure with varying tax brackets and rates. This means the percentage of your income paid in state taxes increases as your income rises. However, specific state tax brackets and rates differ significantly. Some states have a flat tax rate, while others have no income tax at all.
For instance, the Associated Press reported on Georgia’s Republican leaders proposing a new round of state income tax rebates, indicating the presence of a state income tax in Georgia. Conversely, Mississippi’s Republican Governor is pushing for a complete phase-out of their state’s income tax, highlighting the variety in state tax policies. Consulting that state’s Department of Revenue website or a qualified tax professional is recommended to determine the specific tax brackets and rates for a particular state.
Each state has its approach to managing taxes in contrast to federal regulations. The tax structure in your state could include unique brackets or even an entirely different system altogether. Take Colorado, for instance, with its fixed tax rate of 4.4% on taxable income, while other states like Wyoming operate without a state income tax system.
How Does the 2025 Income Tax Bracket Get Adjusted?
Annually, adjustments are made to the federal income tax brackets to align with the prevailing inflation rate. These modifications, officially termed inflation adjustments, are crucial in shaping the tax system.
By adjusting the 2025 tax brackets, individuals can avoid being pushed into a higher tax bracket due to increases in their cost of living, a situation referred to as “bracket creep.” These adjustments can also reduce taxes for individuals whose income has not kept pace with inflation.
What Is An Effective Tax Rate and Marginal Tax Rate?
Calculating your effective tax rate involves determining the portion of your taxable income that goes toward paying taxes. This can be done by dividing the total tax owed indicated in Form 1040 by your overall taxable income.
A marginal tax rate is the tax rate you pay on your last dollar of income. This rate applies to the portion of your income within a specific tax bracket. For example, in the U.S., federal income taxes are progressive, meaning higher earners pay a more significant percentage of their income in taxes. Imagine your income puts you in the 22% tax bracket. This does not mean your entire income is taxed at 22%. Instead, only the portion of your income exceeding the threshold for the previous tax bracket is subject to the 22% rate. The rest of your income is taxed at lower rates according to the lower brackets it falls into.
How to Maximize My Tax Return and Lower the Taxes I Owe
Two ways of reducing your taxes are tax credits and tax deductions. When it comes to managing your taxes, it’s important to understand the distinction between tax credits and tax deductions. Tax credits directly reduce your tax bill, regardless of your tax bracket, by offsetting the amount owed dollar-for-dollar. On the other hand, tax deductions reduce the portion of your taxable income, typically based on your highest federal tax bracket percentage. Leveraging tax credits and deductions effectively is essential to optimize your tax situation.